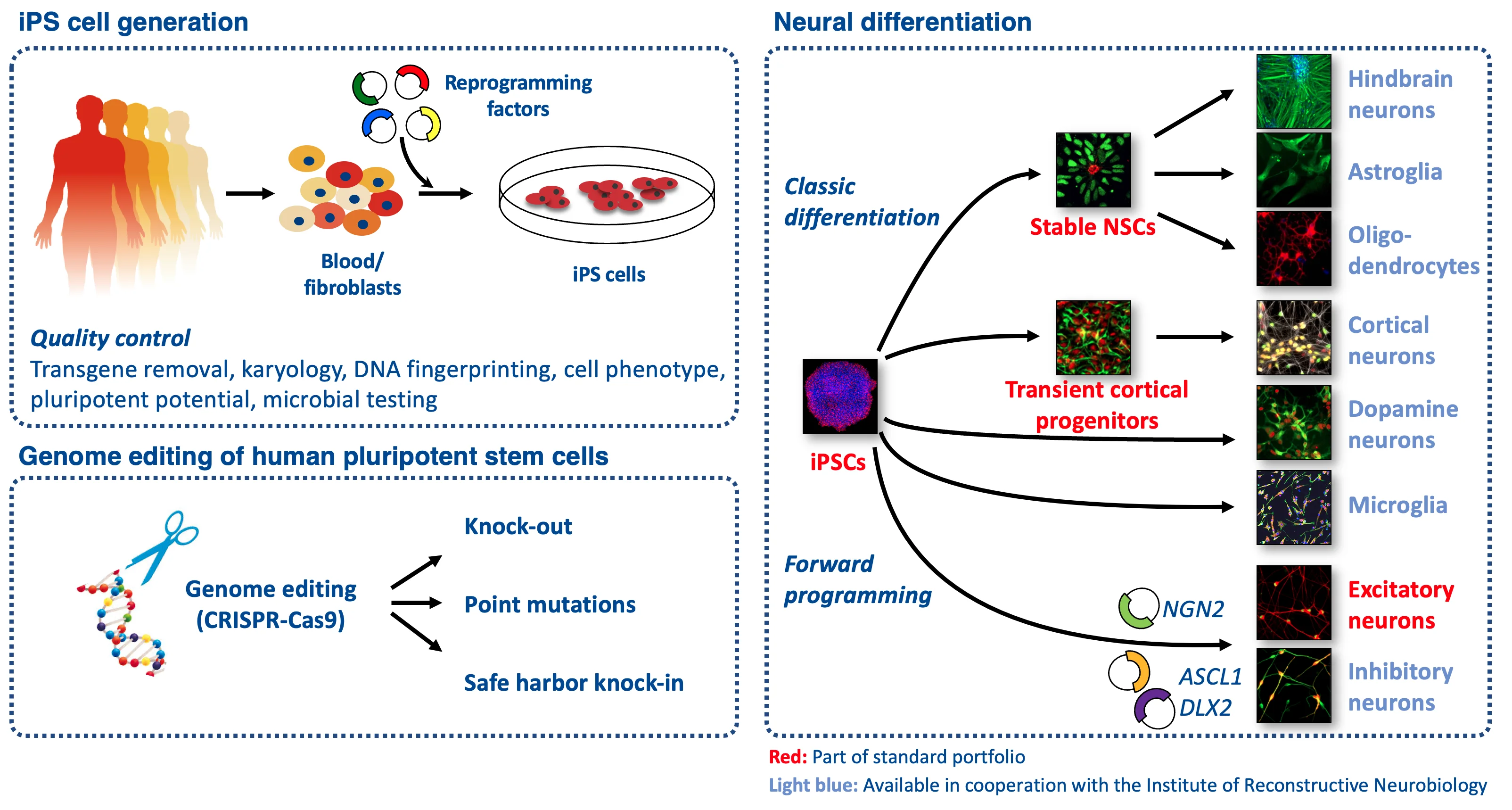
Generation of human iPS cell lines
As starting material for iPS cell derivation we accept skin fibroblasts or peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Donor cells are reprogrammed using the latest Sendai virus-based reprogramming vectors that guarantee transient introduction of transgenes to avoid the stable integration of reprogramming factors. As a standard procedure, we isolate and expand up to five clonal iPS cell lines per subject for cryopreservation and subsequent shipping to the investigator. Depending on the recipients’ demands, selected clones are subjected to standardized quality control regimens (ICC and gene expression profiling for pluripotency analysis, assessment of transgene removal, STR analysis, SNP genotyping).
Genome editing
We also offer genome editing services for the generation of isogenic iPS cell lines with KO alleles, introduced and repaired point mutations as well as the targeted introduction of transgene expression cassettes into the genomic ‘safe harbor’ locus AAVS1.
Neural differentiation
The Cell Programming Core Facility has in-depth expertise in the differentiation of iPS cells into neural precursors as well as terminally differentiated neural cells. Currently, we provide the generation and provision of stable neural precursor cells (NPCs), cortical NPCs and NGN2-induced excitatory forebrain neurons, all of which are available in cryopreserved formats. Please contact us for availability of other neural cell types.


Needful Links
Filippi, Kerstin; Riße, Isabelle; Judge, Luke M.; Conklin, Bruce R.; Fleischmann, Bernd K.; Hesse, Michael (2025): Generation and characterization of a human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) line from a patient with BAG3 P209L myofibrillar myopathy-6. In: Stem cell research 86, S. 103718. DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2025.103718
Filippi, Kerstin; Wiemann, Martin; Fleischmann, Bernd K.; Hesse, Michael (2025): Generation of two isogenic control lines by correcting the BAG3 P209L mutation of human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) lines from patients with myofibrillar myopathy-6. In: Stem cell research 82, S. 103627. DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2024.103627
Hellén, Marianna; Weert, Isabelle; Müller, Stephan A.; Lehtonen, Šárka; Peitz, Michael; Fließbach, Klaus et al. (2025): Inflammation-induced lysosomal dysfunction in human iPSC-derived microglia is exacerbated by APOE 4/4 genotype. In: Journal of neuroinflammation 22 (1), S.147. DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03470-y.
Triantafyllou , Christos; Peitz, Michael; Fleischmann, Bernd K; Rieck, Sarah (2025): Generation of a homozygous DNMT3A knock-out hiPSC line for modeling of cardiovascular diseases associated with clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potenial (2025). In: Stem cell research 86, S. 103707. DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2025.103707
Nießing, B.; Breitkreuz, Y.; Elanzew, A.; Toledo, M.A.S. de; Vajs, P.; Nolden, M. et al. (2025): Automated CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing of human pluripotent stem cells using the StemCellFactory. In: Cytotherapy 27 (5), S220-S221. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2025.03.449
Riße, Isabelle; Filippi, Kerstin; Wiemann, Martin; Fleischmann, Bernd K.; Hesse, Michael (2025): Generation of an isogenic series of genome-edited hiPSC lines with the BAG3P209L-mutation for modeling myofibrillar myopathy 6. In: Stem cell research 82, S. 103641. DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2024.103641
Takalo, Mari; Jeskanen, Heli; Rolova, Taisia; Kervinen, Inka; Hellén, Marianna; Heikkinen, Sami et al. (2025): The protective PLCγ2-P522R variant mitigates Alzheimer's disease-associated pathologies by enhancing beneficial microglial functions. In: Journal of neuroinflammation 22 (1), S. 64. DOI: 10.1186/s12974-025-03387-6.
Zhang, Yanhui; Peitz, Michael; Fleischmann, Bernd K.; Rieck, Sarah (2025): Generation of a genome-edited EMILIN1 (c.1606CT) hiPSC line to investigate aortic aneurysm formation in vitro. In: Stem cell research 86, S. 103708. DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2025.103708
Haubenreich, Carolin; Lenz, Michael; Schuppert, Andreas; Peitz, Michael; Koch, Philipp; Zenke, Martin; Brüstle, Oliver (2024): Epigenetic and Transcriptional Shifts in Human Neural Stem Cells after Reprogramming into Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Subsequent Redifferentiation. In: International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25 (6). DOI: 10.3390/ijms25063214 .
Nießing, Bastian; Breitkreuz, Yannik; Elanzew, Andreas; Toledo, Marcelo A. S. de; Vajs, Peter; Nolden, Marina et al. (2024): Automated CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing of human pluripotent stem cells using the StemCellFactory. In: Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology 12, S. 1459273. DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1459273 .
Querio, Giulia; Antoniotti, Susanna; Levi, Renzo; Fleischmann, Bernd K.; Gallo, Maria Pia; Malan, Daniela (2024): Insulin-Activated Signaling Pathway and GLUT4 Membrane Translocation in hiPSC-Derived Cardiomyocytes. In: International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25 (15). DOI: 10.3390/ijms25158197 .
Yde Ohki, Cristine Marie; McNeill, Rhiannon V.; Vernon, Anthony C.; Smedler, Erik; Michel, Tanja Maria; Peitz, Michael et al. (2024): Correspondence to "Bipolar disorder-iPSC derived neural progenitor cells exhibit dysregulation of store-operated Ca2+ entry and accelerated differentiation" by Hewitt et al. (PMID: 37402854). In: Molecular psychiatry 29 (12), S. 3932–3934. DOI: 10.1038/s41380-024-02602-9 .
Wen, Jianbin; Zellner, Andreas; Braun, Nils Christian; Bajaj, Thomas; Gassen, Nils Christian; Peitz, Michael; Brüstle, Oliver (2023): Loss of function of FIP200 in human pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons leads to axonal pathology and hyperactivity. In: Translational Psychiatry 13 (1), S. 143. DOI: 10.1038/s41398-023-02432-3 .
Alich, Therese C.; Röderer, Pascal; Szalontai, Balint; Golcuk, Kurt; Tariq, Shahan; Peitz, Michael et al. (2022): Bringing to light the physiological and pathological firing patterns of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons using optical recordings. In: Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 16, S. 1039957. DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1039957 .
Gather, Fabian; Ihrig-Biedert, Irmgard; Kohlhas, Paul; Krutenko, Tamara; Peitz, Michael; Brüstle, Oliver et al. (2022): A specific, non-immune system-related isoform of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase is expressed during differentiation of human stem cells into various cell types. In: Cell communication and signaling : CCS 20 (1), S. 47. DOI: 10.1186/s12964-022-00855-x .
Wen, Jianbin; Peitz, Michael; Brüstle, Oliver (2022): A defined human-specific platform for modeling neuronal network stimulation in vitro and in silico. In: Journal of neuroscience methods 373, S. 109562. DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2022.109562 .
Wischhof, Lena; Lee, Hang-Mao; Tutas, Janine; Overkott, Clemens; Tedt, Eileen; Stork, Miriam et al. (2022): BCL7A-containing SWI/SNF/BAF complexes modulate mitochondrial bioenergetics during neural progenitor differentiation. In: The EMBO Journal 41 (23), e110595. DOI: 10.15252/embj.2022110595 .
Wolf, Christina; Pouya, Alireza; Bitar, Sara; Pfeiffer, Annika; Bueno, Diones; Rojas-Charry, Liliana et al. (2022): GDAP1 loss of function inhibits the mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by altering the actin cytoskeleton. In: Commun Biol 5 (1), S. 541. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03487-6 .
Cenini, Giovanna; Hebisch, Matthias; Iefremova, Vira; Flitsch, Lea J.; Breitkreuz, Yannik; Tanzi, Rudolph E. et al. (2021): Dissecting Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis in human 2D and 3D models. In: Molecular and cellular neurosciences 110, S. 103568. DOI: 10.1016/j.mcn.2020.103568 .
Manstein, Felix; Ullmann, Kevin; Kropp, Christina; Halloin, Caroline; Triebert, Wiebke; Franke, Annika et al. (2021): High density bioprocessing of human pluripotent stem cells by metabolic control and in silico modeling. In: Stem cells translational medicine 10 (7), S. 1063–1080. DOI: 10.1002/sctm.20-0453 .
Schmid, Benjamin; Holst, Bjørn; Clausen, Christian; Bahnassawy, Lamiaa; Reinhardt, Peter; Bakker, Margot H. M. et al. (2021): Generation of a set of isogenic iPSC lines carrying all APOE genetic variants (Ɛ2/Ɛ3/Ɛ4) and knock-out for the study of APOE biology in health and disease. In: Stem cell research 52, S. 102180. DOI: 10.1016/j.scr.2021.102180 .
PD Dr. Michael Peitz
Life and Brain, building 76
Venusberg-Campus 1
53127 Bonn
Monika Veltel
Life and Brain, building 76
Venusberg-Campus 1
53127 Bonn
Cornelia Thiele
Life and Brain, building 76
Venusberg-Campus 1
53127 Bonn
Prof. Dr. Oliver Brüstle
Life and Brain, building 76
Venusberg-Campus 1
53127 Bonn
Acknowledgements
Administration Medical Faculty
Documents
The Core Facilities thank the German Research Foundation for continuous support.